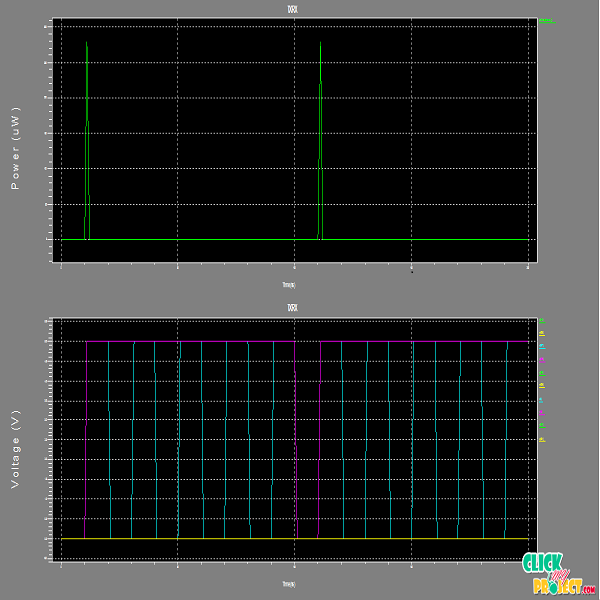
Description
In a high-performance VLSI design, the clock network consumes a significant amount of power. While most existing methodologies use voltage-mode (VM) signaling, these clock distributions lose a tremendous amount of dynamic power to charge/discharge the large global clock capacitance. New circuit approaches for current-mode (CM) clocking save significant clock power, but have been limited to only symmetric networks, while most application specific integrated circuits have asymmetric clock distributions.