Top-k Similarity Join in Heterogeneous Information Networks
Our Price
₹3,500.00
10000 in stock
Support
Ready to Ship
Description
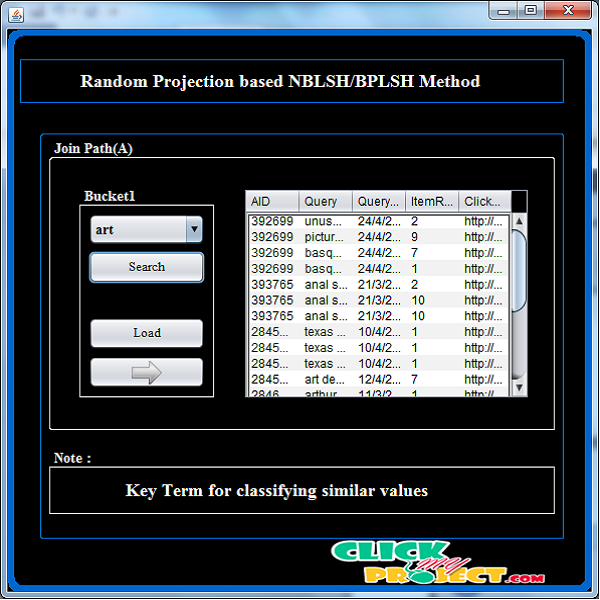
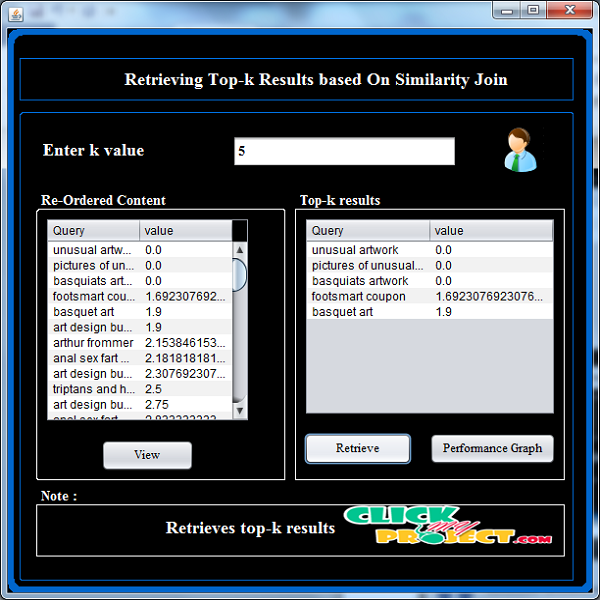
Similarity search is a primitive operation in database and Web search engines. With the advent of large-scale heterogeneous information networks that consist of multi-typed, interconnected objects, such as the bibliographic networks and social media networks, it is important to study similarity search in such networks. In this paper, we propose a path-based similarity join (PS-join) method to return the top k similar pairs of objects based on any user specified join path in a heterogeneous information network. We study how to prune expensive similarity computation by introducing bucket pruning based locality sensitive hashing (BPLSH) indexing. Different semantic meanings behind paths are not taken into consideration. Thus they cannot be directly applied to heterogeneous networks. Our proposed method uses “nearby buckets” in a hash table to generate candidate object pairs. With the advent of large-scale heterogeneous information networks that consist of multi-typed, interconnected objects, such as the bibliographic networks and social media networks, it is important to study similarity search in such networks. Intuitively, two objects are similar if they are linked by many paths in the network. However, most existing similarity measures are defined for homogeneous networks. Different semantic meanings behind paths are not taken into consideration. Thus they cannot be directly applied to heterogeneous networks. In this paper, we study similarity search that is defined among the same type of objects in heterogeneous networks. Moreover, by considering different linkage paths in a network, one could derive various similarity semantics. Therefore, we introduce the concept.