Scalable Application-Dependent Diagnosis of Interconnects of SRAM-Based FPGAs
Our Price
₹3,000.00
10000 in stock
Support
Ready to Ship
Description
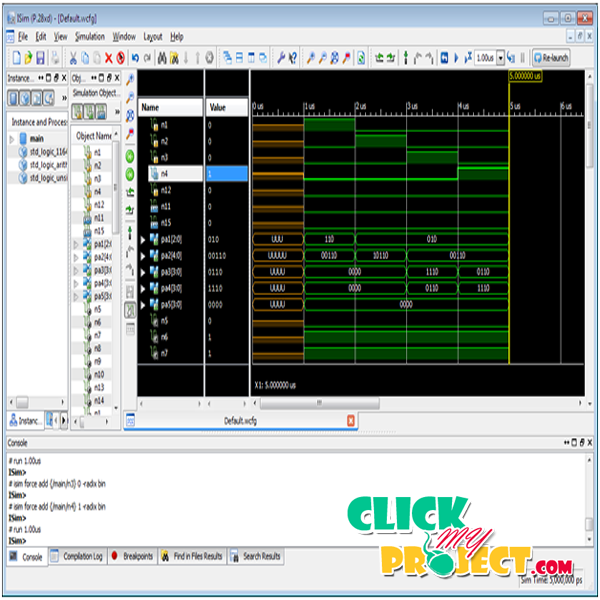
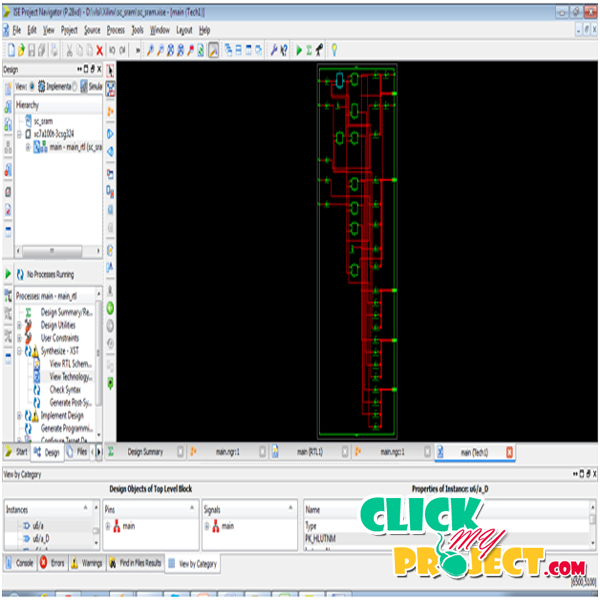
Very-large-scale integration (VLSI) is the process of creating an integrated circuit by combining thousands of transistors into a single chip. The microprocessor is a VLSI device. VLSI’s design tools eventually included not only design entry and simulation but eventually cell-based routing (chip compiler), a data path compiler, SRAM and ROM compilers, and a state machine compiler. The tools were an integrated design solution for IC design and not just point tools, or more general purpose system tools. Diagnosis (detection and location) is a name for design techniques that add certain testability features to a microelectronic hardware product design. The premise of the added features is that they make it easier to develop and apply manufacturing tests for the designed hardware. The fault identification mainly based on the circuit analysis based process in the SRAM –FPGA based LUT architecture and not network based process. This architecture presents a new method for diagnosing multiple faults in an application-dependent interconnect of a SRAM-based FPGA. For fault detection, the proposed technique retains the original interconnect configuration and modifies the function of the LUTs using the new LUT programming function 1-Bit Sum Function in addition, it utilizes features such as branches in the nets as well as the primary IOs of the FPGAs. This paper presents a new method for diagnosing (detection and location) multiple faults in an application-dependent interconnect of a SRAM-based FPGA. The proposed technique retains the original interconnect configuration and modifies the function of the LUTs using the new LUT programming function 1-Bit Sum Function (1-BSF); in addition, it utilizes features such as branches in the nets as well as the primary (unused) IOs of the FPGAs. The locations of multiple faults are hierarchically identified using thewalking-1 test set and an adaptive approach for the interconnect structure. Net ordering independence is accomplished by utilizing features such as the presence of paths of nets that are either disjoint or joint between the primary input and at least one primary output. VLSI s is the field which involves packing more and more logic devices into smaller and smaller areas. Nearly all modern chips employ VLSI architectures. This paper grants a new logic for diagnosing several faults in an application-dependent interrelate of a SRAM-based FPGA Modifies the function of the LUTs using the new LUT programming function 1-Bit Sum Function in addition, it operates features such as divisions in the nets as well as the crucial IOs of the FPGAs. Diagnosis is a name for proposal method that add certain testability features to a microelectronic hardware product scheme. The principle of the added structures is that they make it relaxed to develop and apply making tests for the deliberate hardware. DFT methods can be more or less diagnostics-friendly. The related objectives of DFT are to simplify/simplify fail data collection. Diagnostics to an extent that can permit intelligent failure inquiry (FA) sample selection, as well as increase the price, correctness, speed, and material of diagnostics and FA. The programmable communicate accounts for more than 80 percent of the FPGA programmable resources .
Tags: 2014, VHDL Network Projects