Robust Retinal Vessel Segmentation via Locally Adaptive Derivative Frames in Orientation Scores
₹4,500.00
10000 in stock
SupportDescription
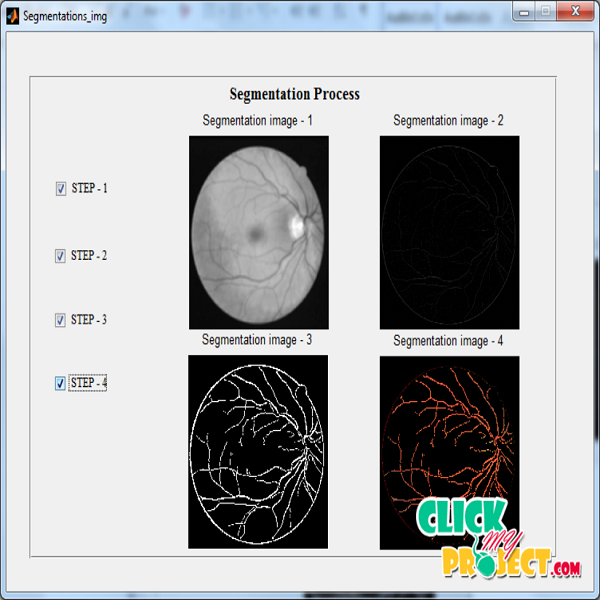
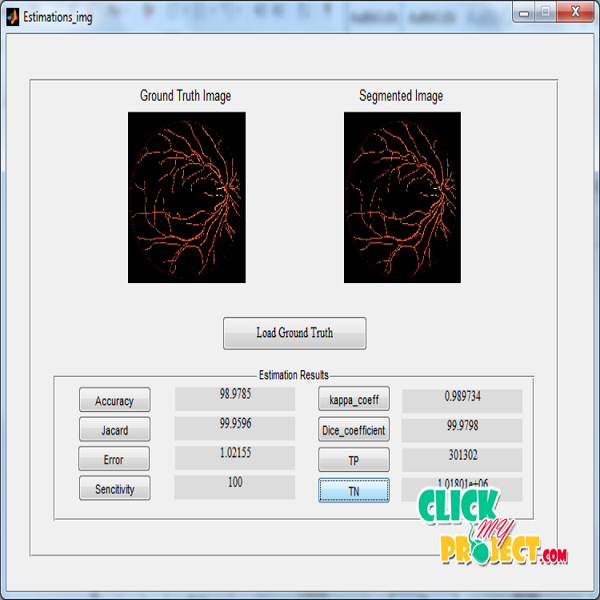
A robust and fully automatic filter-based approach for retinal vessel segmentation. We proposenew filters based on 3D rotating frames in so-called orientation scores, which are functions on the Lie-group domain of positions and orientations R 2* S 1 . By means of a wavelet-type transform,a 2D image is lifted to a 3D orientation score, where elongated structures are disentangled into their corresponding orientation planes. In the lifted domain R2 * S1, vessels are enhancedby means of multi-scale second-order Gaussian derivatives per-pendicular to the line structures. More precisely, we use aleft-invariant rotating derivative (LID) frame, and a locallyadaptive derivative (LAD) frame. The LAD is adaptive to thelocal line structures and is found by eigensystem analysis of theleft-invariant Hessian matrix (computed with the LID). After multi-scale filtering via the LID or LAD in the orientation scoredomain, the results are projected back to the 2D image plane giving us the enhanced vessels. Then a binary segmentationis obtained through thresholding. The proposed methods are validated on six retinal image datasets with different image types, on which competitive segmentation performances are achieved. In particular, the proposed algorithm of applying the LAD filter on orientation scores (LAD-OS) outperforms most of the state-of-the-art methods. The LAD-OS is capable of dealing with typically difficult cases like crossings, central arterial reflex, closely parallel and tiny vessels. The high computational speed of the proposed methods allows processing of large datasets in a screening setting