Modeling and Analysis of Class EF and Class E/F Inverters With Series-Tuned Resonant Networks
₹4,500.00
10000 in stock
SupportDescription
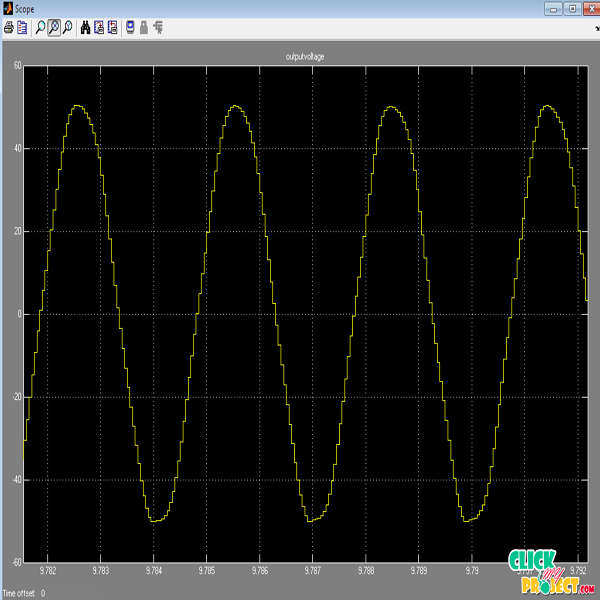
Resonant inverter is the generic name for a type of high frequency switching topology used in many of Spellman’s supplies. Resonant switching topologies are the next generation of power conversion circuits, when compared to traditional pulse width modulation (PWM) topologies. Resonant-based supplies are more efficient than their PWM counterparts. This is due to the zero current and/or zero voltage transistor switching that is inherent in a resonant supplies design. This feature also provides an additional benefit of eliminating undesirable electromagnetic radiation normally associated with switching supplies. The switching devices in converters with a PWM control can be gated to synthesize the desired shape of the output voltage or current. But at high switching frequency, the switches are subjected to a high voltage stress, and the switching power loss also increases. The disadvantages of PWM control can be eliminated by using resonant pulse inverter. Thus operation at very high frequencies and too rapid on/off control. Features of this inverter topology include low semiconductor voltage stress, small passive energy storage requirements, fast dynamic response, and good design flexibility. Class E Resonant Inverters are theoretically capable of delivering any power to a load and achieve 100% efficiency at any frequency of operation. In practice efficiency in the “high 90’s” can be achieved into megahertz frequencies regardless of inverter output powers. This topology has a hybrid inverters that are combination of class EF and class E/F inverters. Thus results efficiency is high, output power and power capability can be improved.