Least Power Point Tracking Method for Photovoltaic Differential Power Processing Systems
Our Price
₹4,500.00
10000 in stock
Support
Ready to Ship
Description
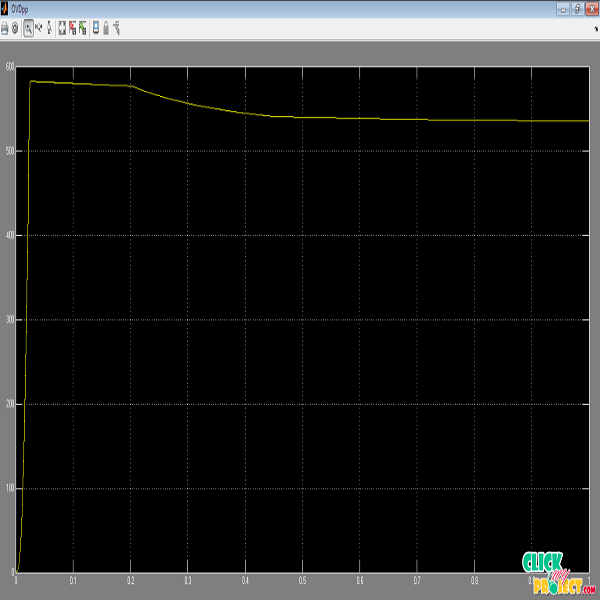
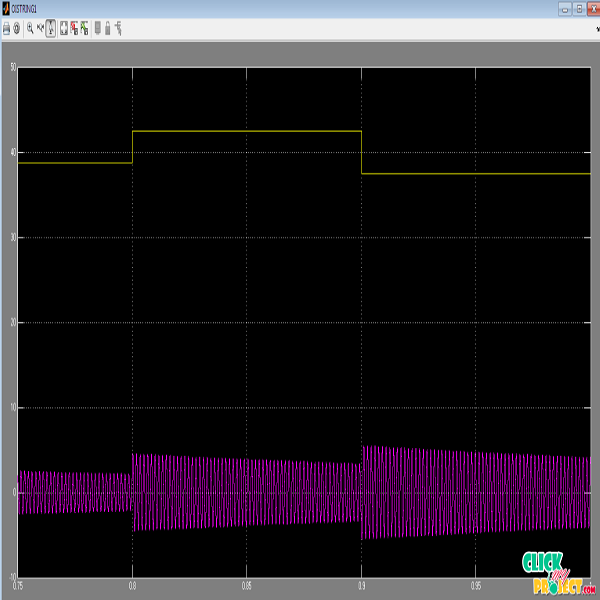
In this proposed implementation is based on differential power processing (DPP) systems, that area promising architecture for future photovoltaic (PV) power systems that achieve high system efficiency through processing a faction of the full PV power, while achieving distributed local maximum power point tracking (MPPT). In the PV-to-bus DPP architecture, the power processed through the DPP converters depends on the string current, which must be controlled to minimize the power processed through the DPP converters. A real-time least power point tracking (LPPT) method is proposed to minimize power stress on PV DPP converters. Mathematical analysis shows the uniqueness of the least power point for the total power processed through the system. The perturb and-observe LPPT method is proposed that enables the DPP converters to maintain optimal operating conditions, while reducing the total power loss and converter stress. This work validates through simulation and experimentation that LPPT in the string-level converter successfully operates with MPPT in the DPP converters to maximize output power for the PVto-bus architecture. Hardware prototypes were developed and tested at 140 W and 300 W, and the LPPT control algorithm showed effective operation under steady-state operation and an irradiance step change.