iPath Path Inference in Wireless Sensor Networks
Our Price
₹3,500.00
10000 in stock
Support
Ready to Ship
Description
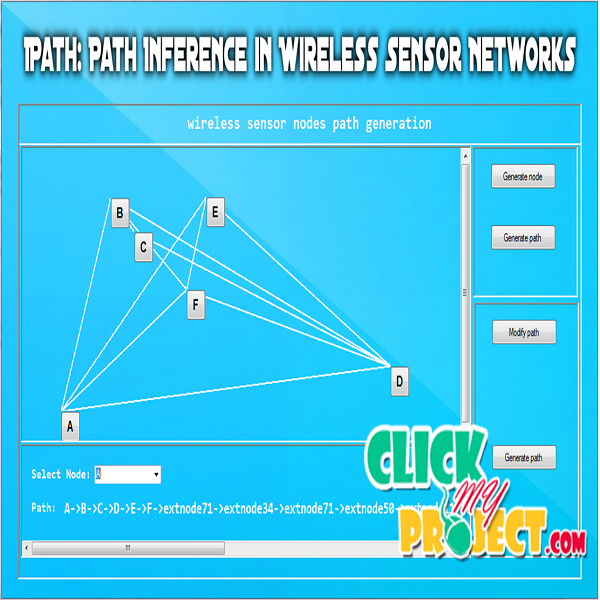
A wireless sensor network (WSN) are spatially distributed autonomous sensors to monitor physical or environmental conditions, such as temperature, sound, pressure, etc. and to cooperatively pass their data through the network to a main location. The more modern networks are bi-directional, also enabling control of sensor activity. The WSN is built of “nodes” – from a few to several hundreds or even thousands, where each node is connected to one (or sometimes several) sensors. Each such sensor network node has typically several parts: a radio transceiver with an internal antenna or connection to an external antenna, a microcontroller, an electronic circuit for interfacing with the sensors and an energy source, usually a battery or an embedded form of energy harvesting. Recent Wireless Sensor networks (WSNs) are becoming increasingly complex with the growing network scale and the dynamic nature of wireless communications. The system proposes a novel path inference approach to reconstructing the per-packet routing paths in dynamic and large-scale networks. It includes a novel design of a lightweight hash function for verification of the inferred paths. In order to further improve the inference capability as well as the execution efficiency. It achieves much higher reconstruction ratios under different network settings compared to other state-of-the-art approaches.
Tags: 2015, Dotnet, Network Projects