Compression of Hyperspectral Images Containing a Subpixel Target
Our Price
₹3,000.00
10000 in stock
Support
Ready to Ship
Description
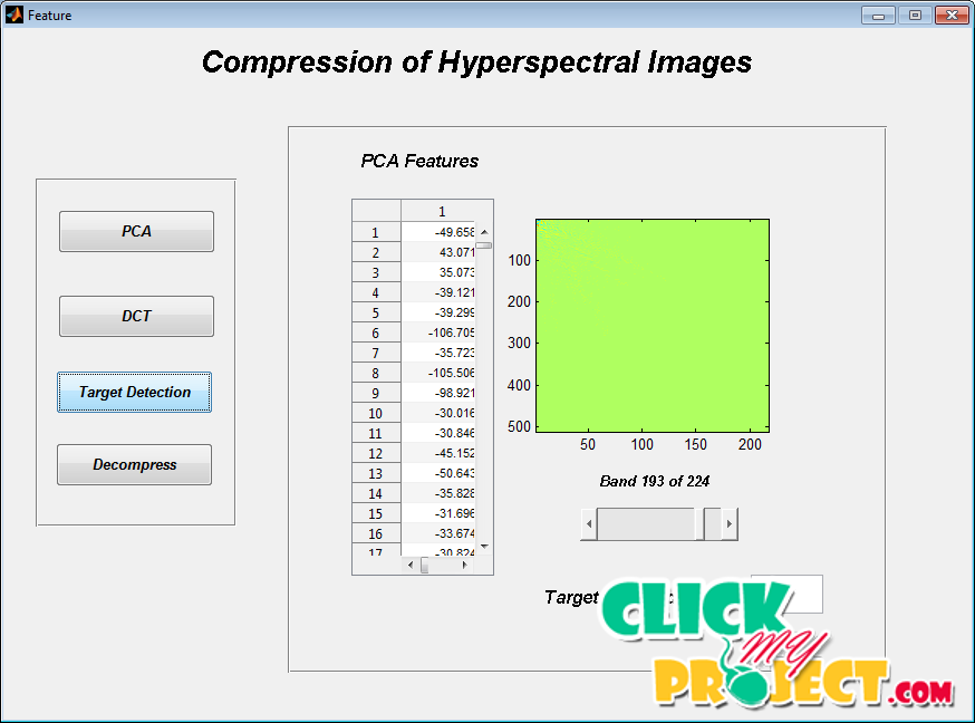
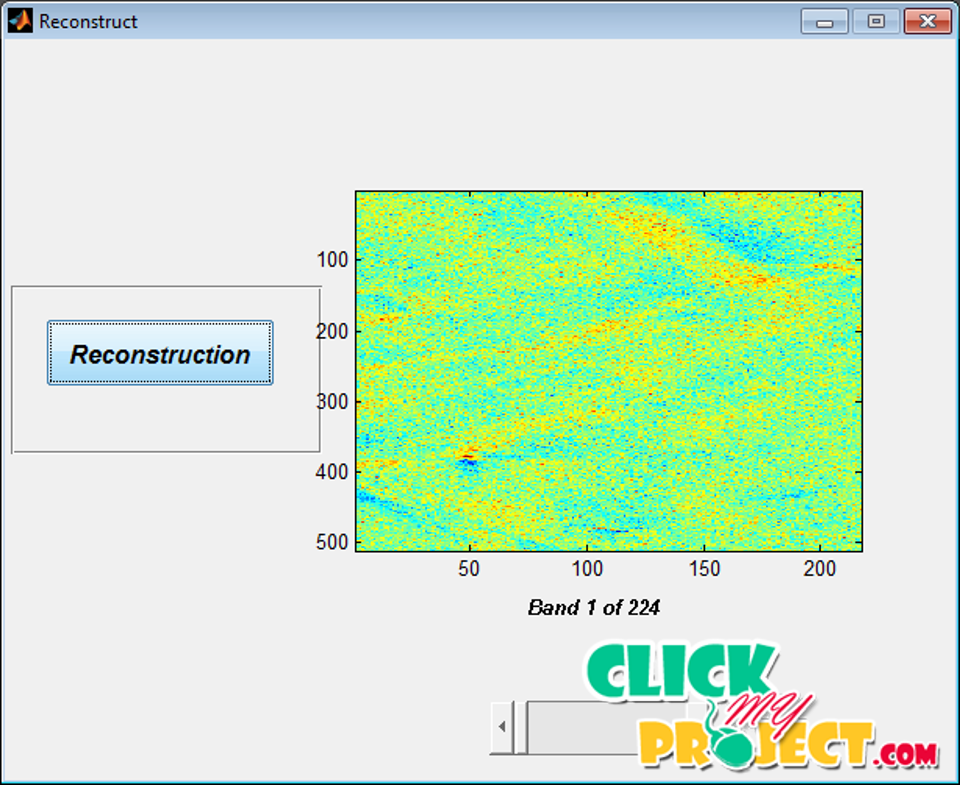
Hyperspectral images show similar statistical properties to natural grayscale or color photographic images. However, the classification of hyperspectral images is more challenging because of the very high dimensionality of the pixels and the small number of labeled examples typically available for learning. These peculiarities lead to particular image processing problems, mainly characterized by indetermination and complex manifolds. Hyperspectral imagery is a new type of high-dimensional image data which is now used in many Earth-based and planetary exploration applications. Many efforts have been devoted to designing and developing compression algorithms for hyperspectral imagery. Unfortunately, most available approaches have largely overlooked the impact of mixed pixels and subpixel targets, which can be accurately modeled and uncovered by resorting to the wealth of spectral information provided by hyperspectral image data. Compression techniques able to reduce significantly the large volume of information contained in hyperspectral data while, at the same time, being able to retain information that is crucial to deal with mixed pixels and subpixel targets. In proposed work, Principal Component analysis has been proposed where background information of the HSI are characterized by second-order statistics. The extracted features are subtracted from the original image in order to obtain the residual image. Finally the Discrete cosine transforms has been applied to get the compressed image. This process is outperformed with the prior work. This compression method is kept simple for fast processing and implementation, and considers lossy compression only on the spectral axis.