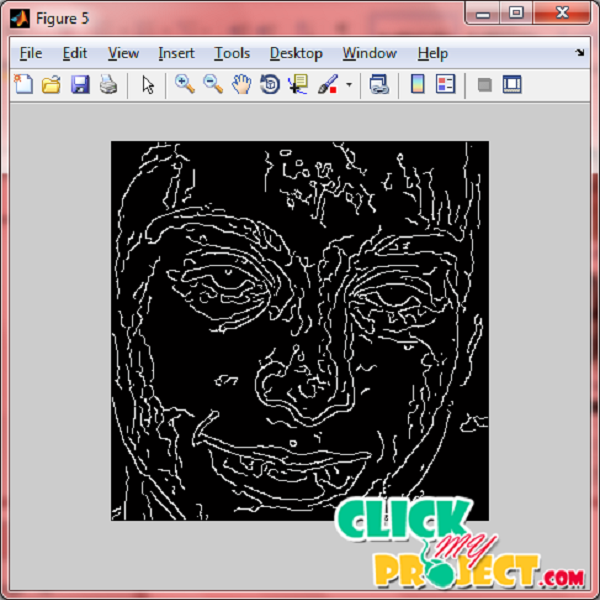
Description
Face recognition is the process of identifying one or more people in images or videos by analyzing and comparing patterns. Algorithms for face recognition typically extract facial features and compare them to a database to find the best match. Face recognition is an important part of many biometric, security, and surveillance systems, as well as image and video indexing systems. Improvements in discriminative power come at a computational cost and with a risk of over-fitting. The system proposes a new approach to dense feature extraction for age face recognition. This approach consists of two steps. First, an encoding scheme is devised that compresses high-dimensional dense features into a compact representation by maximizing the intrauser correlation. The human face holds important amount of information and attributes such as expression, gender and age. The vast majority of people are able to easily recognize human traits like emotional states, where they can tell if the person is happy, sad or angry from the face. Likewise, it is easy to determine the gender of the person. However, knowing person‟s age just by looking at old or recent pictures for them is often a bigger challenge. Our objective in this thesis is to develop a human age estimator from face images. Given a face image of the person, we label it with an estimated age. Aging is non-reversible process. Human face characteristics change with time which reflects major variations in appearance. The age progression signs displayed on faces are uncontrollable and personalized such as hair whitening, muscles dropping and wrinkles. The aging signs depend on many external factors such as life style and degree of stress. For instance smoking causes several facial characteristics changes.