Automated Detection of Driver Fatigue Based on Entropy and Complexity Measures
₹3,000.00
10000 in stock
SupportDescription
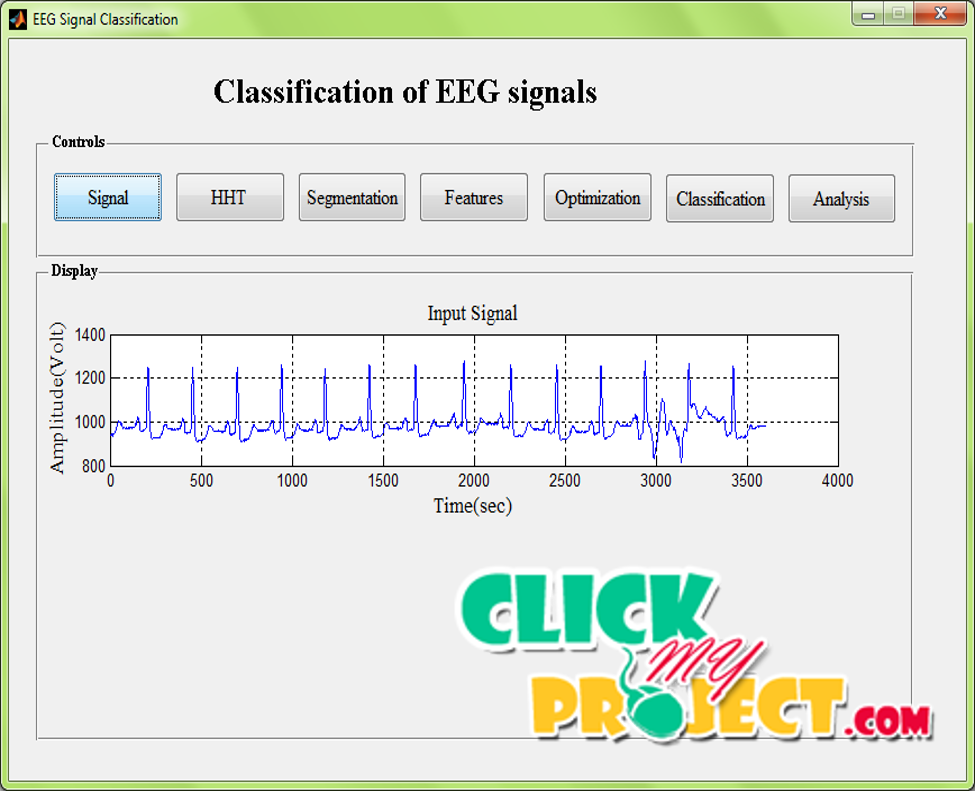
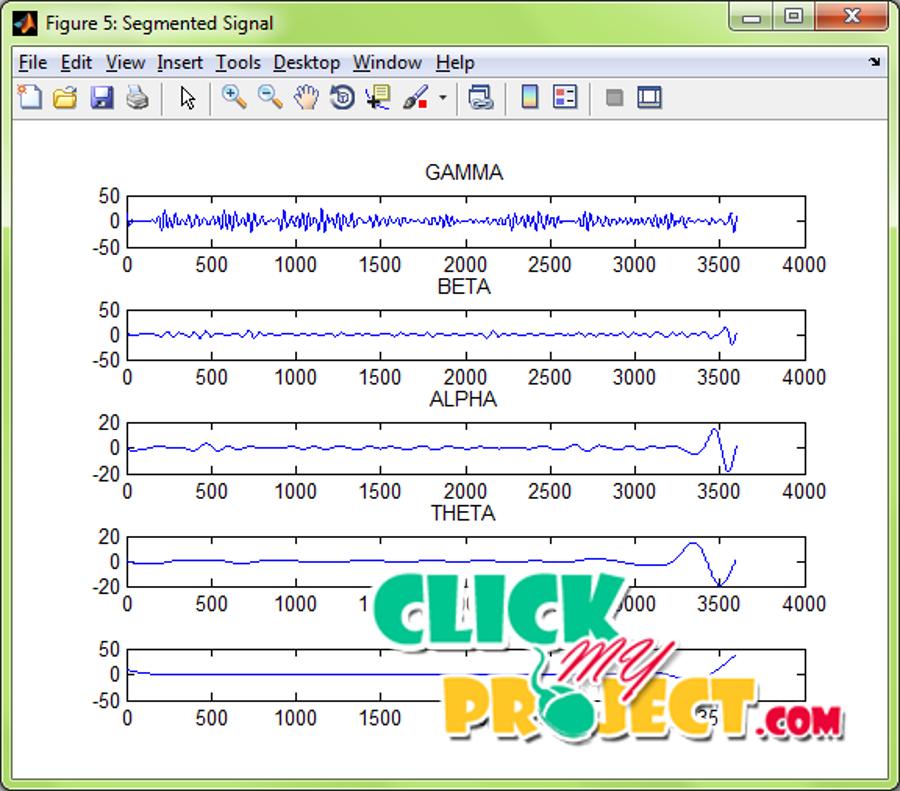
Electroencephalogram (EEG) is a recording of the electrical activity of the brain from the brain waves produced by the electrical current passing through the nerves during the brain activities. The classification of the EEG signals can be helpful in monitoring patients and identification of the different brain activities. The EEG signals were classified based on the statistical features obtained from the different segments of the EEG signals. The EEG signals were segmented with the help of Hilbert–Huang transform. The segmented signals were then classified using Neural Network classifier. The Neural Network is a pattern recognition tool that identifies the type of the signals by analyzing the patterns of the features. Epileptic fatigue occur intermittently and unpredictably, mindless seizure detection in EEG cassettes is highly required. In our method, the HHT based time-frequency representation (TFR) has been considered as time-frequency image (TFI), the segmentation of TFI has been effected based on the frequency-bands of the rhythms of EEG signals, the histogram of grayscale sub-images has been denoted. STFT is unavoidable in trade-off between time and regularity firmness, the wavelet theory is limited by the fundamental uncertainty principle, the struggle of the WVD is the severe cross terms as indicated by the existence of negative power for some frequency assortments. The identification of the fatigue based on the features extracted is more efficient compared to the other feature extraction methods employed for the analysis of the signals.