A Novel Energy-Efficient Clustering Based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing f or Cognitive Radio Sensor Networks
Our Price
₹3,500.00
10000 in stock
Support
Ready to Ship
Description
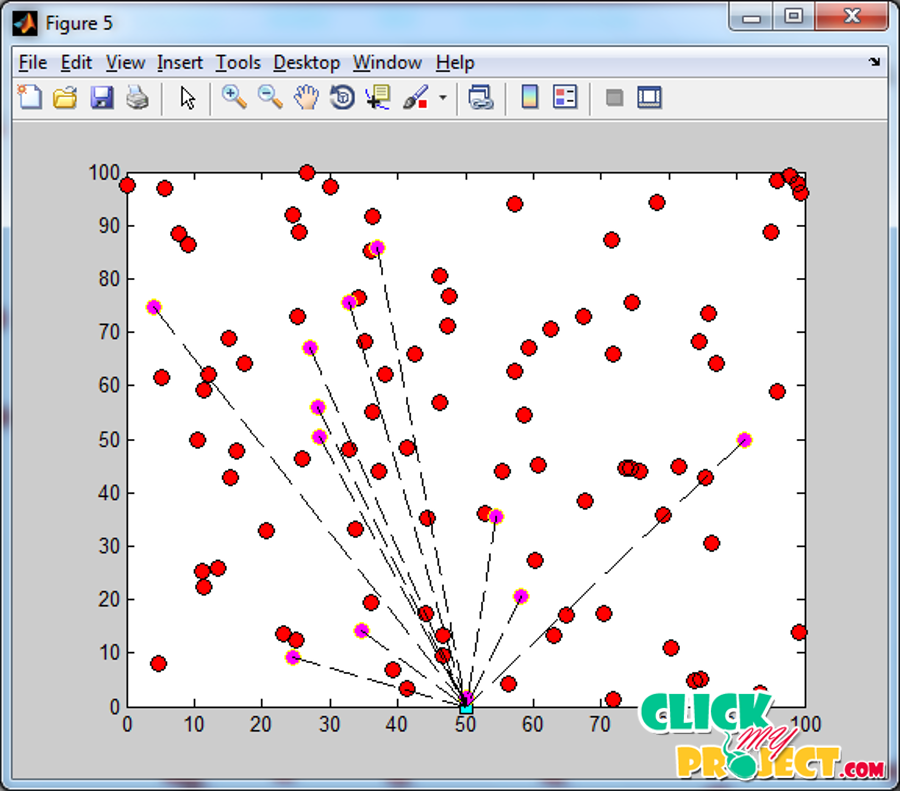
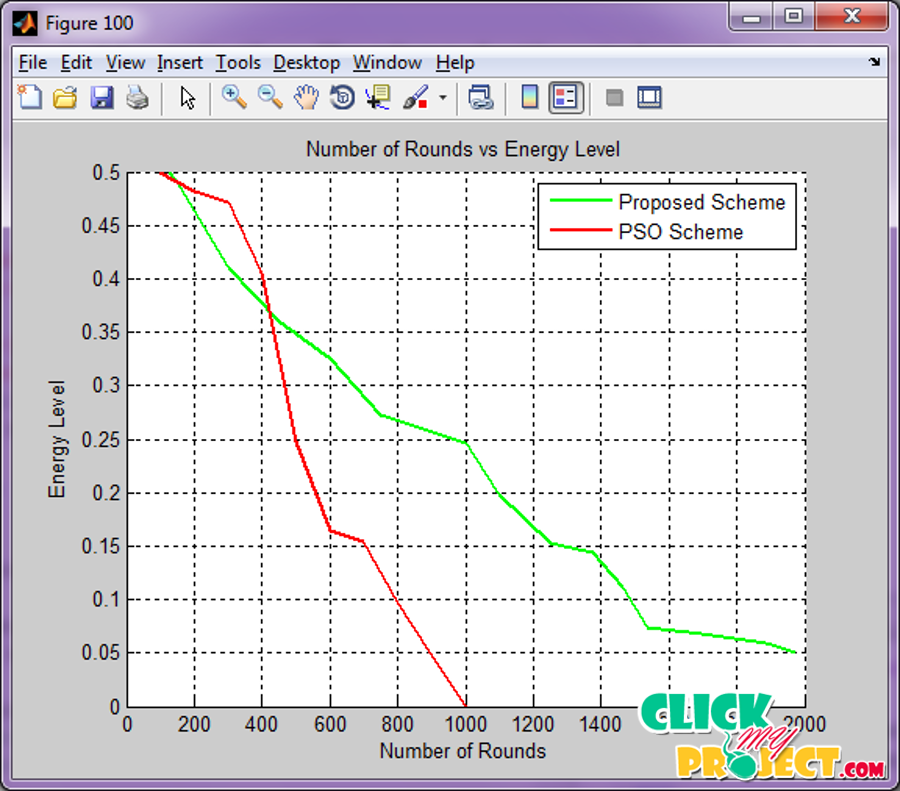
In cognitive radio systems, secondary users can be coordinated to perform cooperative spectrum sensing so as to detect the primary user more accurately. By separating all the secondary users into a few clusters and selecting the most favorable user in each cluster to report to the common receiver, the proposed method can exploit the user selection diversity so that the sensing performance can be enhanced. Increasing energy efficiency, network lifetime, network stability, and optimal cluster-head selection process, this paper proposes a novel energy efficient clustering based on cooperative spectrum sensing (ECS) for CRSNs. Advances in wireless sensor network (WSN) technology has providing the readiness of small and low-cost sensor nodes with aptitude of sensing various types of physical and environmental surroundings. This is based on slanted election prospects of each node to become cluster head conferring to the enduring energy in each node. The recreation results shows that cooperative spectrum sensing (ECS) yields extended stability section for higher values of extra energy taken by more powerful lumps. A heterogeneous-aware protocol to prolong the time break before the death of the first node, which is important for many tenders where the retort from the sensor network must be unfailing. The sensors are self-ruling small devices with several limitations like the battery power, division capacity, communication range and memory. In this paper proposed a new data furthering access to be improved the lifetime of wireless sensor network using entries. This will devour less energy in long reserve communication. Model results show the protocol offer a batter presentation. cooperative spectrum sensing (ECS) stochastic collection head range algorithm is prolonged by adjusting the threshold T (n). Considering these limitations, simulation results shows that the proposed practice REAP 1 and REAP 2 could better reduce energy eating and prolong lifetime of the wireless sensor network.
Tags: 2015, Matlab, Network Projects