A Comparative Study of Power Supply Architectures in Wireless EV Charging Systems
Our Price
₹3,500.00
10000 in stock
Support
Ready to Ship
Description
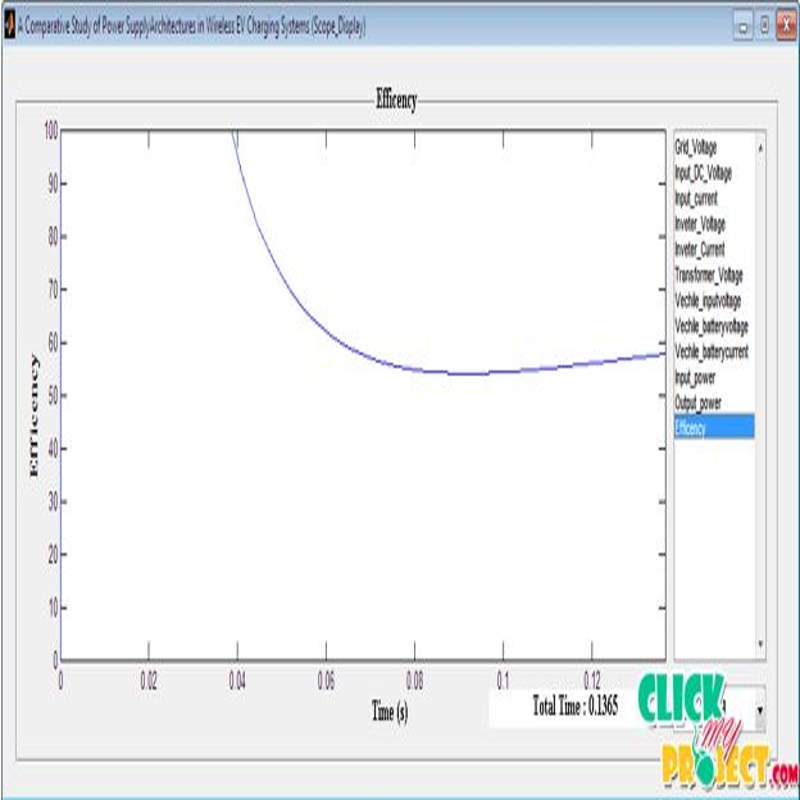
Wireless inductive power transfer is a transformational and disruptive technology that enables the reliable and efficient transfer of electrical power over large air gaps for a host of unique applications. One such application that is now gaining much momentum worldwide is the wireless charging of electric vehicles (EVs). A charging system of an electric vehicle includes a drive battery storing electric power for driving a motor of the electric vehicle, a heater heating the drive battery, an electric power supply device converting electric power supplied from outside the electric vehicle and supplying the electric power to the drive battery or the heater, a contactor activating or deactivating a connection between the drive battery and the electric power supply device, temperature detector detecting a temperature of the drive battery, and controller controlling the contactor and the heater based on the temperature. The controller controls the contactor so as to deactivate the connection and conducts electricity to the heater when the temperature is less than a first predetermined temperature, and controls the contactor so as to activate the connection when the temperature is the first predetermined temperature or greater. In our proposed we design the inverter for wireless charging system. In these processes we design the basic LLC inverter, the source and load is connected by air medium using the mutual induction for charging the battery. In these process get the voltage from grid and then convert to the DC the using the LLC converter to boost and transmit the voltage with source to vehicle. It is the give the better output for charging the electrical vehicle.
Tags: 2015, Matlab, Power Electronics